Design research stands at the confluence of creativity, technology, and human behavior, striving to understand how users interact with products, systems, and services. In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful tool—one that promises to revolutionize the way we gather, analyze, and interpret user data. Among these innovations is the advent of AI-generated users: synthetic personas and simulated user data created by sophisticated algorithms. Although this technology offers the allure of streamlined processes, cost efficiency, and rapid insights, a growing body of research and practical experience calls into question its overall effectiveness.
This comprehensive article examines the case against AI-generated users and outlines robust alternatives for design research. We explore the limitations of synthetic user data, delve into the ethical and methodological challenges they present, and offer detailed case studies and comparative analyses. Our aim is to provide design researchers, UX professionals, and industry leaders with an in-depth, academically rigorous perspective that will empower them to make informed decisions and enhance the authenticity and ethical integrity of their research practices.
Understanding the Role of AI-Generated Users in Design Research
The integration of artificial intelligence into design research has given rise to methods that generate user personas and simulate user behavior through data-driven algorithms. Proponents argue that AI-generated users can expedite research processes and provide immediate insights across diverse user groups. However, this technological leap is accompanied by significant challenges that warrant a careful reexamination of its use in the design process.
Overview of AI-Generated Users
AI-generated users are created using machine learning algorithms that process vast amounts of data—ranging from historical user interactions to social media trends—to construct synthetic profiles. These profiles are intended to mimic real user behaviors and preferences, thereby assisting in the development of products that cater to broad demographic and psychographic characteristics.
The benefits of this approach include:
• Streamlined research processes
• Rapid generation of multiple user personas
• Potential cost savings during early-stage design
• The ability to simulate various user scenarios for testing and validation
Despite these potential advantages, there are several critical concerns that arise when relying solely on synthetic data.
Critical Limitations of AI-Generated Users
- Lack of Authenticity
AI-generated profiles, while data-driven, can struggle to capture the full spectrum of human emotions, lived experiences, and nuanced behaviors. Authentic user insights are often lost when the focus shifts from personal narratives to algorithmically generated generalizations. - Overgeneralization and Stereotyping
Algorithms work on the basis of patterns found in existing data. When historical data contains inherent biases or oversimplifications, the resulting user profiles may inadvertently reinforce stereotypes or provide an overly homogenized view of diverse user needs. - Ethical Challenges
The data used to generate synthetic profiles can raise significant ethical issues, particularly around privacy, consent, and the inadvertent propagation of bias. The opaque nature of some AI systems further complicates accountability and ethical oversight. - Methodological Shortcomings
Traditional design research methods—such as ethnography, in-depth interviews, and contextual inquiries—allow researchers to uncover subtle insights that are often missed by AI systems. The absence of human empathy and context in AI-generated data limits its applicability in addressing real-world design challenges.

The Importance of Authentic User Research
Authentic user research is the bedrock of effective design. Real users bring rich, qualitative insights that drive empathy, innovation, and ultimately, user-centered design. When researchers rely exclusively on AI-generated users, they risk sacrificing the depth and authenticity that come from direct interaction. Maintaining a balance between technological efficiency and genuine human insight is crucial for creating products that truly resonate with users.
Case Study: The Pitfalls of AI-Generated Users in Design
A multinational technology firm recently sought to accelerate its design research process by implementing an AI system to generate user personas for a new product line. The AI-generated profiles were meant to encapsulate a wide range of user behaviors and preferences. However, during subsequent product testing, the firm encountered a significant disconnect between the synthetic insights and the actual needs and behaviors of its target audience.
Key Findings from the Case Study
• Misalignment with User Reality
The AI-generated personas, while diverse on paper, failed to capture the nuances of the real-world user experience. This resulted in product features that did not adequately address key pain points.
• Reinforcement of Biases
The algorithm, trained on historical datasets that contained ingrained biases, inadvertently perpetuated stereotypes. Minority perspectives were underrepresented, leading to a skewed understanding of the user base.
• Ethical Dilemmas
The use of datasets containing sensitive information without explicit user consent raised privacy concerns. The lack of transparency in the AI model further complicated the ability to assess and mitigate these ethical issues.

This case study underscores the inherent risks associated with relying solely on AI-generated users. It reinforces the need to critically assess the limitations of synthetic data and to seek alternative methodologies that prioritize authenticity and ethical considerations.
Ethical and Methodological Concerns in AI-Generated User Research
Integrating AI-generated users into design research is not merely a technical decision—it also carries significant ethical and methodological implications that must be addressed to maintain the integrity of the research process.
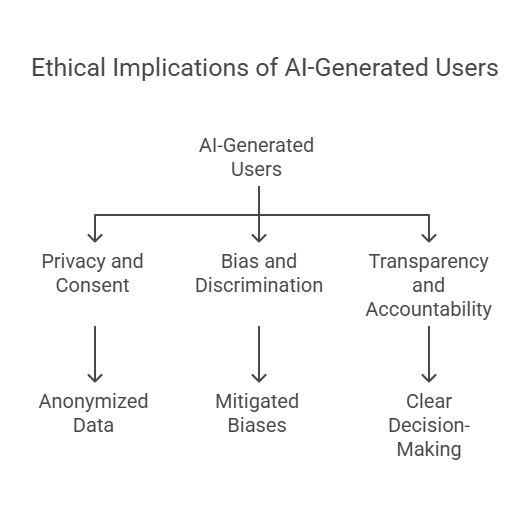
Ethical Implications
The ethical concerns surrounding AI-generated users are multifaceted and include:
• Privacy and Consent
AI systems often rely on large datasets that may contain personally identifiable information. Without explicit consent from individuals whose data is used, the practice raises serious privacy issues. Researchers must ensure that data is anonymized and used ethically.
• Bias and Discrimination
Because AI algorithms are trained on historical data, they are vulnerable to perpetuating existing biases. If these biases are not actively mitigated, they can result in discriminatory practices and misrepresentations that negatively impact design outcomes.
• Transparency and Accountability
Many AI systems operate as “black boxes,” where the decision-making process is not fully transparent. This lack of transparency can make it difficult to identify and rectify errors, further compounding ethical concerns.
For an in-depth exploration of these issues, the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) provides an excellent resource on AI ethics.
Methodological Limitations
From a methodological standpoint, AI-generated users exhibit several shortcomings:
• Loss of Nuanced Insights
Traditional methods such as ethnography and user interviews capture complex, context-dependent data that AI systems may overlook. These methods provide the narrative depth necessary for understanding user motivations and behaviors.
• Overemphasis on Quantitative Data
AI systems excel at processing large volumes of quantitative data but struggle with the subtleties of qualitative research. This can lead to a disproportionate focus on numbers over narratives, resulting in an incomplete picture of user experiences.
• Reduced Flexibility
The rigidity of AI-generated profiles means they are less adaptable to evolving research questions or unforeseen insights that emerge during the research process. In contrast, traditional methods allow for real-time adjustments and deeper exploration of emerging themes.
Balancing the efficiency of AI with the depth of traditional methods is critical. Researchers must remain vigilant to ensure that the adoption of new technologies does not compromise the quality of user insights.
Emerging Alternatives for Design Research
Given the significant drawbacks of relying solely on AI-generated users, it is essential to explore alternative methodologies that can deliver authentic, ethical, and actionable insights. The following approaches offer promising pathways to enhance design research.
Mixed Methods Approach
A mixed methods approach combines both qualitative and quantitative research techniques, harnessing the strengths of each to provide a more comprehensive view of user behavior.
Key Benefits:
• Depth and Breadth: Qualitative interviews and ethnographic studies provide rich contextual data, while quantitative surveys capture broader statistical trends.
• Enhanced Validation: Cross-referencing findings from different methods helps validate insights and ensure consistency.
• Flexibility: This approach allows researchers to adjust methods as new insights emerge, facilitating a dynamic research process.
Best Practices for Mixed Methods:
- Begin with Qualitative Research: Conduct in-depth interviews, focus groups, and ethnographic observations to gather detailed user narratives.
- Design Complementary Quantitative Surveys: Create surveys that quantify key qualitative findings, enabling statistical validation.
- Triangulate Data: Use multiple sources of data to cross-verify insights and identify inconsistencies.
Ethnographic and Participatory Research
Ethnographic research involves immersing oneself in the user’s environment to observe real-life behaviors and contexts. Participatory research extends this approach by actively involving users in the research process, thereby ensuring that their voices are central to the design process.
Advantages:
• Real-World Insights: Observing users in their natural settings provides an authentic view of their challenges and motivations.
• Empowerment: Involving users directly in the research process fosters a sense of ownership and enhances the relevance of design solutions.
• Rich Data: The narrative depth obtained through these methods can reveal underlying emotional and cultural factors that influence behavior.
These methods, though traditionally more time-consuming, yield insights that are crucial for designing truly user-centric products.
Hybrid Approaches with AI Augmentation
While the pitfalls of AI-generated users are significant, AI still holds tremendous potential when used to augment rather than replace human-driven research methods. Hybrid approaches combine the computational power of AI with the nuanced insights provided by traditional research methods.
Applications of AI Augmentation:
• Sentiment Analysis: AI can process large volumes of user feedback—such as online reviews and social media comments—to identify prevailing sentiments and emerging trends.
• Data Visualization: Advanced AI-driven visualization tools can help researchers interpret complex data sets, making it easier to identify actionable insights.
• Pattern Recognition: Machine learning algorithms can detect subtle patterns in quantitative data, which can then be validated through qualitative research.
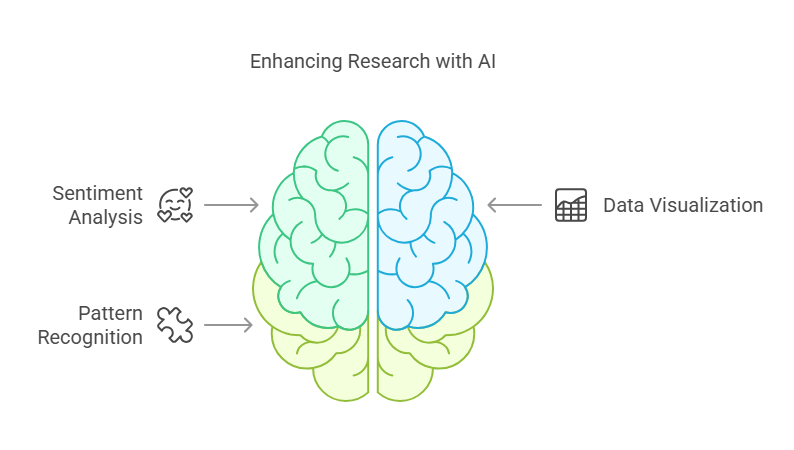
By integrating AI augmentation with traditional techniques, design researchers can benefit from both rapid data processing and the rich, contextual insights provided by human interaction.
Comparative Analysis: AI-Generated Users vs. Traditional Methods
A clear understanding of the strengths and limitations of different research methodologies is essential for making informed design decisions. The following comparative analysis outlines the primary differences between AI-generated users and traditional research methods.
- Authenticity
• AI-Generated Users: Rely on synthetic, data-driven profiles that may lack the complexity of real user experiences.
• Traditional Methods: Directly capture authentic user behaviors and emotions through face-to-face interaction. - Flexibility
• AI-Generated Users: Tend to be inflexible, with profiles that do not adapt easily to new research findings or changing contexts.
• Traditional Methods: Allow for iterative exploration and adaptation as new insights emerge during the research process. - Ethical Considerations
• AI-Generated Users: Pose significant ethical challenges related to privacy, consent, and bias due to their reliance on historical data.
• Traditional Methods: Typically adhere to established ethical guidelines with informed consent and transparent data collection practices. - Efficiency and Cost
• AI-Generated Users: Offer rapid data generation and may reduce costs during early research phases.
• Traditional Methods: Can be resource-intensive but provide richer, more actionable insights that justify the investment.
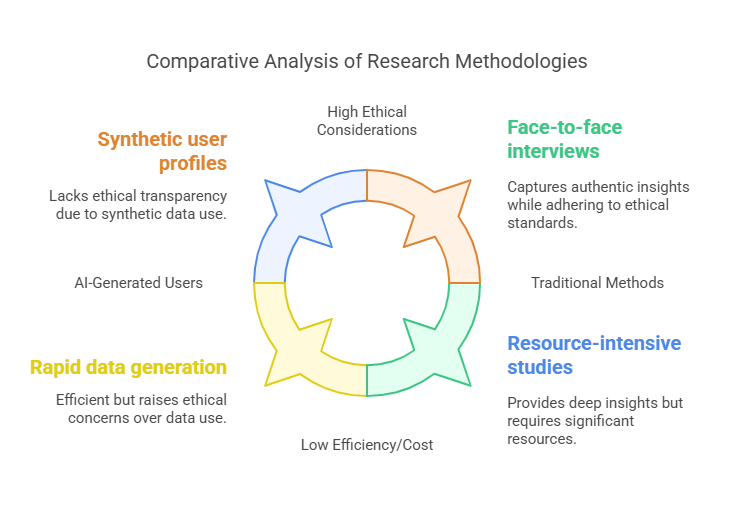
Although AI-generated users offer potential efficiency gains, the long-term drawbacks in authenticity, ethical standards, and flexibility often render them less effective as standalone research tools.
Integrating AI with Traditional Techniques: A SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis can help to clarify the potential benefits and risks of integrating AI-generated data with conventional research methods.
Strengths:
• Rapid data processing and trend analysis capabilities.
• The ability to handle large data sets that can identify macro-level trends.
Weaknesses:
• Inability to capture the nuanced context and complexity of user experiences.
• Potential reinforcement of existing biases due to reliance on historical data.
Opportunities:
• Development of hybrid research models that combine AI’s analytical power with human empathy.
• Innovation in data visualization and pattern recognition to support deeper insights.
Threats:
• Overreliance on AI might lead to the neglect of essential human-centered research methods.
• Misinterpretation of AI-generated findings without sufficient qualitative validation.

This analysis emphasizes the need for a balanced approach that leverages AI’s strengths while mitigating its weaknesses through complementary traditional methodologies.
Implications for the Future of Design Research
The debate over AI-generated users has far-reaching implications for the future of design research and the broader technology landscape. As AI continues to evolve, its integration into research practices must be guided by the following principles:
- Prioritizing Authenticity
Ensuring that user research remains grounded in real-world interactions is essential. Authentic insights are crucial for developing products that genuinely meet user needs. - Ethical AI Practices
Establishing and adhering to robust ethical frameworks is vital for protecting user privacy, preventing bias, and maintaining transparency in data use. As researchers and designers, we must advocate for ethical AI practices that safeguard user rights. - Continuous Methodological Innovation
The dynamic nature of design research calls for ongoing experimentation with new methodologies. Hybrid models that combine the best of AI and human insight are likely to define the future of the field. - Transparency and Accountability
Future AI systems must be designed with transparency in mind. Researchers should be able to understand and, if necessary, challenge the underlying algorithms to ensure ethical and unbiased outcomes.

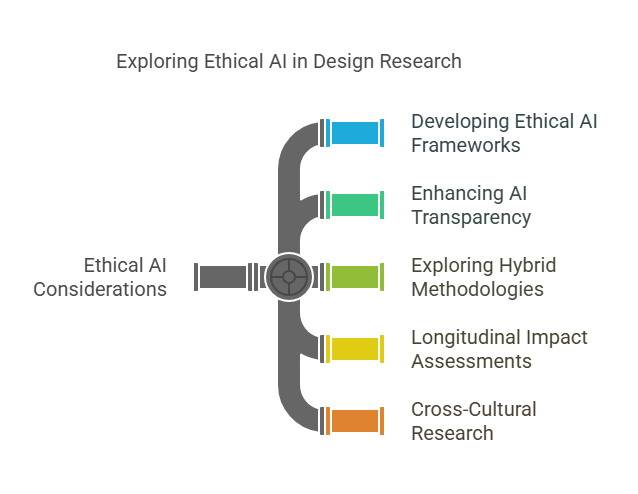
Given the challenges associated with AI-generated users, several areas require further investigation to ensure that design research remains ethical, effective, and user-centric:
- Developing Ethical AI Frameworks
Future research must focus on creating robust ethical guidelines for AI in user research. This includes establishing protocols for data privacy, consent, and bias mitigation. - Enhancing AI Transparency
Studies are needed to improve the transparency of AI algorithms. Understanding the inner workings of these systems will enable researchers to identify potential pitfalls and rectify errors. - Exploring Hybrid Methodologies
Further investigation into hybrid research models that integrate AI with traditional qualitative methods is essential. Such research can help determine the optimal balance between computational efficiency and human insight. - Longitudinal Impact Assessments
Research should assess the long-term impact of using AI-generated data on product design, user satisfaction, and overall market success. Understanding these effects will inform best practices for future projects. - Cross-Cultural Research
As global markets evolve, research must examine how AI-generated user data performs across different cultural contexts. This will help ensure that design research methodologies remain inclusive and globally relevant.
Case Study: Bridging the Gap with Hybrid Approaches
A leading e-commerce platform experienced significant challenges during a period of rapid digital transformation. Initially, the company relied heavily on AI-generated user profiles to guide product development. However, the approach soon revealed critical gaps between synthetic insights and real user needs. Recognizing these shortcomings, the research team pivoted to a hybrid approach that combined AI-driven analytics with direct user engagement methods such as in-depth interviews and ethnographic research.
Outcomes of the Hybrid Approach:
• Improved Accuracy: Integrating qualitative data helped refine AI-generated trends, resulting in user profiles that more accurately reflected real-world behavior.
• Enhanced User Engagement: Direct user involvement fostered trust and provided deeper insights, leading to a product that resonated more effectively with the target audience.
• Iterative Feedback Loops: The hybrid model enabled continuous improvement through ongoing feedback, allowing the design team to iterate and refine product features in real time.
Key Lessons Learned:
• AI-generated data is most effective when used to complement, not replace, human-centered research.
• A balanced approach that integrates both quantitative and qualitative insights leads to more robust and actionable design outcomes.
• Ethical and methodological rigor must remain at the forefront of any research strategy to ensure long-term success.
Practical Guidelines for Implementing Alternative Research Methods
For practitioners seeking to transition away from an overreliance on AI-generated users, the following step-by-step guidelines can help create a more balanced and effective design research strategy:
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide:
- Conduct a Comprehensive Audit
• Review existing research methodologies and identify areas where AI-generated data is predominant.
• Assess the limitations and biases present in your current data collection processes. - Integrate Qualitative Research
• Incorporate methods such as ethnographic studies, focus groups, and one-on-one interviews to capture rich, contextual insights.
• Ensure that user narratives form a core component of your research findings. - Establish a Hybrid Research Model
• Combine AI-driven data analytics with traditional research methods to validate findings and uncover deeper insights.
• Leverage advanced analytical tools for pattern recognition while relying on human interpretation for context. - Implement Ethical Safeguards
• Develop and adhere to strict guidelines for data privacy, consent, and transparency.
• Regularly review and update ethical protocols to keep pace with evolving technologies. - Monitor and Iterate
• Continuously assess the impact of your research methods through iterative feedback loops.
• Be prepared to adjust your strategy based on emerging insights and changing market conditions.

Key Ethical Considerations:
• Prioritize informed consent and ensure that all user data is collected ethically.
• Actively work to identify and mitigate biases in both AI-generated and traditional research data.
• Maintain transparency in data collection and analysis processes, making it easier for stakeholders to understand research outcomes.
Integrating Advanced Analytical Tools with Human Insights
As design research evolves, the integration of advanced analytical tools with traditional methods offers a promising avenue for innovation. By combining the computational power of AI with the depth of human insight, researchers can harness the best of both worlds.
Key Technologies in AI Augmentation:
• Natural Language Processing (NLP)
– Analyze vast amounts of user feedback, reviews, and social media data to extract sentiment and thematic patterns.
• Machine Learning Algorithms
– Identify subtle patterns in large datasets that can inform design decisions.
• Data Visualization Software
– Transform complex datasets into intuitive visual representations that facilitate rapid understanding and decision-making.
These tools, when used as augmentation rather than replacement, empower researchers to uncover insights that might otherwise remain hidden, ensuring that design research remains both efficient and deeply human-centered.
Balancing Technology with Human Insight
In an era defined by rapid technological advancements, the role of AI in design research continues to spark debate. While AI-generated users may offer the promise of speed and efficiency, their limitations in authenticity, ethical integrity, and methodological flexibility cannot be overlooked. Real user insights—gathered through immersive, human-centered research methods—remain the gold standard for developing products that truly resonate with users.
Key Insights:
• AI-generated users provide rapid, data-driven insights but lack the nuanced understanding of real human experiences.
• Methodological limitations and ethical challenges, including privacy concerns and potential biases, undermine the effectiveness of synthetic user profiles.
• Hybrid approaches that integrate AI augmentation with traditional qualitative methods offer a balanced and effective alternative.
• Ongoing research and the development of ethical frameworks are critical to advancing design research in a responsible manner.
• Practical, step-by-step guidelines can help practitioners transition to methodologies that prioritize authenticity and ethical rigor.
We urge design researchers, UX professionals, and industry leaders to critically evaluate their current methodologies. Embrace hybrid research models that combine the efficiency of AI with the depth of human insight, and commit to ethical practices that honor the complexity of the user experience. Subscribe to our newsletter and join our community of innovators to stay updated on the latest trends and insights in design research.
The journey toward truly user-centric design is complex and multifaceted. As AI continues to evolve, its role in design research must be carefully balanced with methods that capture the rich, authentic experiences of real users. By integrating advanced analytical tools with traditional, empathetic research techniques, we can build a future where design not only meets but exceeds user expectations.

Leave a comment